What are Endocannabinoids
The Endocannabinoid System Explained
The Endocannabinoid system (ECS) is one of the human body’s biological systems discovered fairly recently, in 1990. Like the pulmonary system, circulatory, skeletal, muscular, and skeletal systems all have their specific functions, so does the Endocannabinoid system.
The ECS is responsible for regulating the activity of all the other biological systems which ensures their proper functioning. This means our ECS affects everything the human body does and is affecting us every second. How come we know so little about such an important part of our lives?
A brief history of the Endocannabinoid system
As scientists were trying to figure out how cannabis works, mainly how Tetrahydrocannabinol influences us, they found the receptors to which THC can bind if consumed. Hence naming them cannabinoid receptors. To their surprise, they found the cannabinoid receptors scattered all over the human body.
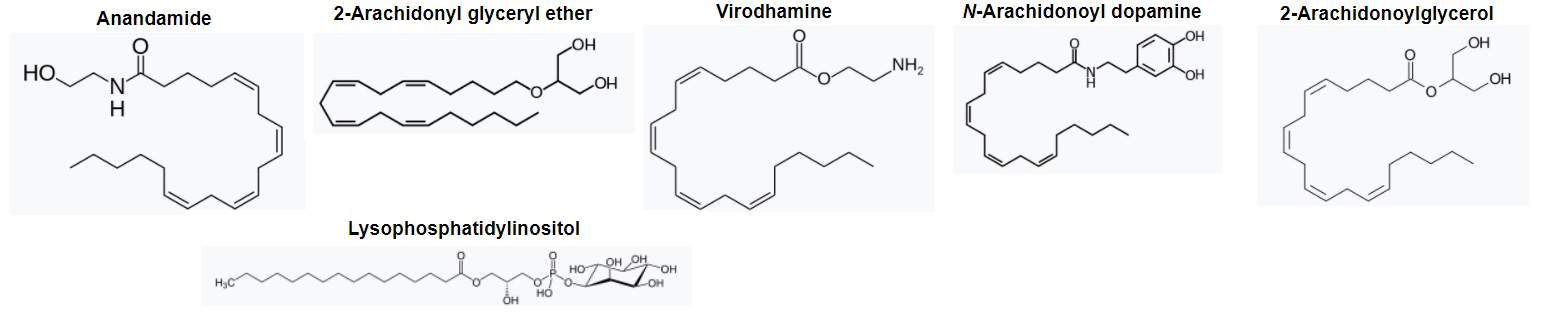
And even more stunning, they discovered an endogenous ligand, for which the cannabinoid receptors exist. Later, they found more chemicals produced by our bodies that interact with cannabinoid receptors and named them endocannabinoids.
The first identified endocannabinoid, anandamide, was documented in 1992. The researchers were amazed how anandamide structurally resembles THC, and how similar it is in activity when it binds to receptors. Soon, they uncovered another compound, 2-AG, mostly located in our brain which has a great affinity to cannabinoid receptors. Later, more followed.

What are Endocannabinoids?
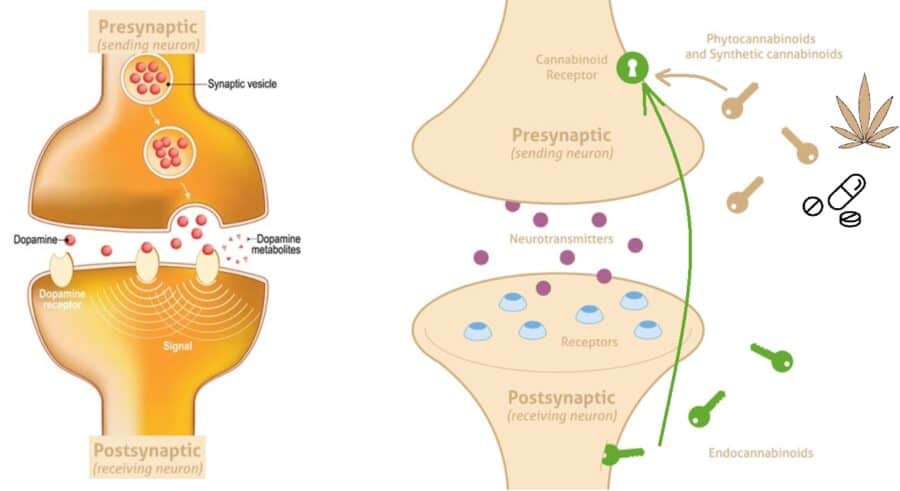
These fascinating compounds are produced in our bodies and act as signaling molecules, similar to neurotransmitters. Like neurotransmitters, they are produced in the neuron cells and their role is to send messages from one neuron to another. However, endocannabinoids are produced in the postsynaptic neuron, contrary to neurotransmitters which are produced in the presynaptic neuron.
By going in the opposite direction in neurons the endocannabinoids bind to cannabinoid receptors regulating the amount of neurotransmitter release in the presynaptic neuron.
With this counter grade signaling, endocannabinoids like Anandamide and 2-AG serve as a blocking-releasing mechanism. Their role is to limit neurotransmitter activity by tapering their release. Doing so they are slowing down the neurotransmitter-receptor interaction which prevents the nervous system from getting burned out.
The Role of the Human Endocannabinoid System
Endocannabinoids, cannabinoid receptors, and enzymes are in charge of taking care that every function in our body works properly. The Endocannabinoids are biosynthesized on demand through enzymatic production in the postsynaptic neuron.
In case neurotransmitters are required to send signals, the endocannabinoids are not produced. If the neurotransmitters are too active, endocannabinoids are made and sent into the presynaptic neuron to limit neurotransmitter activity.
Examples of how endocannabinoids system regulates our bodies:
- If we get in danger, our body starts to send adrenaline through our neurons. Dopamine signals our body to breath faster, the heart rate rises, we become more alert and focused. Once out of danger, we do not require dopamine anymore. Endocannabinoids are deployed and stop dopamine from being released. We are calmed down.
- When it gets dark at night, our body starts to send melatonin through our neurons. Melatonin signals our body to slow down and rest, we become tired and sleepy. In the morning, endocannabinoids send messages to melatonin to stop releasing. We become awake and it’s time to get up!
After the situation settles, endocannabinoids are not required anymore and get degraded by enzymes. Enzymes like FAAH (Fatty acid amide hydrolase) and MAGL (Monoacylglycerol) also make part of the endocannabinoid system, along with CB1 and CB2 receptors and the endocannabinoids. The enzymes are a very important part of our ECS since they make the breakdown of endocannabinoids possible, which basically means the enzymes shut down the endocannabinoid activity.

The Endocannabinoid System and CBD Oil
As we found out, the endocannabinoid system has a very big influence on our life. What happens if the system does not work as it should?
The consequences of a distorted endocannabinoid system are seen in:
- Unexplained mood swings and sudden changes behavior
- Irregular sleep patterns and eating disorders
- Migraines and other forms of headaches
- Autoimmune diseases and Nervous system diseases
The reason for the malfunction of an endocannabinoid system can be neither:
- Cannabinoid receptors can get worn out due to stress, lack of sleep, etc.. and are unable to receive endocannabinoid signaling
- Enzymes are not working correctly, (likely because of unhealthy diet or alcohol and drug abuse, poisoning) and too many endocannabinoid are present which result in a hyperactive endocannabinoid tone
- Endocannabinoid deficiency, meaning the body does not produce enough of its own cannabinoids to support other processes.
And for all the reasons above, CBD oil comes into play. CBD can solve many issues by simply putting our endocannabinoid system in check. Cannabidiol can influence all 3 parts of our ECS:
- it binds to CB1 and CB2 receptor without activating them, which puts them to rest
- CBD supports the body to produce more endocannabinoids
- Cannabidiol diminishes enzymatic degradation of endocannabinoids, increasing their count
Conclusion
In the perfect scenario, we would not need CBD to supplement our endocannabinoid system. With a healthy diet, daily exercise, unpolluted air, and water, a consistent sleep regimen,… the production of our own cannabinoids would be sufficient.

However, the modern lifestyle which we live today shows quite the opposite. Lots of processed food, long work hours, stress on every corner, all take a toll on our endocannabinoid system. With little time to care for ourselves, CBD offers the ultimate solution to boost our ECS to make our minds and body happy.
Essentia Pura is one of the leading CBD manufacturers in Europe and can supply CBD in various forms for every situation. From full-spectrum CBD oil to CBD isolate, we bring to the market CBD products for all kinds of consumers.
